While appearance of the
corona virus Covid-19 is unrelated to how digitally advanced our world is, its
spread should have something to do with how day to day transactions among people
take place. The Chinese city Wuhan’s experience has suggested that despite an
environment where people do most of their transactions online from their jobs to shopping, the spread was inevitable because nobody knew initially that the virus was being transferred from one person to others. However, once that was discovered, common sense suggests that a world where people were digitally connected and physically distant, rest of the world could have prevented the spread viably.
environment where people do most of their transactions online from their jobs to shopping, the spread was inevitable because nobody knew initially that the virus was being transferred from one person to others. However, once that was discovered, common sense suggests that a world where people were digitally connected and physically distant, rest of the world could have prevented the spread viably.
You might have heard
expert sociologists and analysts blame digital marketing revolution to have created a social
distance among people by providing them opportunities to work, shop, and
conduct business from home. So, the hypothesis that a more digitally advance
world could have prevented the outbreak seems to have some truth. The internet
revolution means people communicate increasingly online from distant locations
substantially decreasing physical contact among people.
Digitalization affects
businesses in two important ways: it affects how employees and other people
working in the company interact; and how customers interact with the business
and other customers. Some businesses have a digital model which significantly reduces
customers' physical interaction with the business by accepting orders and
payment online and then delivering products to home. Amazon is an appropriate
example of this. But as you might have guessed, Amazon still employs many
people who are working with it physically all the time. Because, lockdowns and
curfews mean no or little transport, home deliveries might still be a problem
for such businesses.
The other type of businesses is the reverse of the first category—they let their employees work from home but the customers still have to reach out. In both cases, however, physical interaction among people decreases.
With the fears surrounding
the virus, people are themselves avoiding crowds and are trying go out
less and less besides the lockdowns and shutdowns forcing them to stay home.
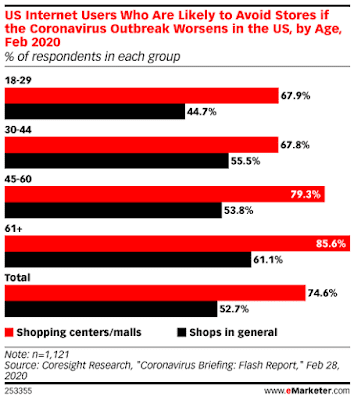
Moreover, as these data
from e-marketer
suggest, customers are more likely to avoid visiting a store than shopping
online. This also implies that people are willingly shifting towards online
channels; customers perceive them to be safer. This does come with some logic
in fact because doctors are strictly suggesting social distance and preventing going
out.
So, what we are trying to
understand is how the situation would have been different given more regions and economies
were digitally connected; for example, 80 or 90 percent of customers shopping
online and larger share of worldwide employees working from home. The above-mentioned
facts suggest that this outbreak should have impacted less adversely had the customers,
business, NGOs, and government agencies been more digitally active rather than reliant on physical connectivity.
There are several side effects of the virus to consider, however, that affect online business at least as bad as brick-and-mortar.
First, lockdowns—curfews in some countries and regions—mean no transport, which
means products can’t be delivered to homes. Second, for some businesses a large
number of employees have to come to work physically even if the outbound supply
chain is digitalized as we talked about Amazon earlier. Third, and the most
significant, supply chains are what is most affected by the outbreak. Even if a
business is solely online, it still has to depend on suppliers, transporters
and other supply chain partners that are shutdown due the corona virus outbreak.
Thus, while it is yet difficult
to conclude if a more digital world would have been less severely affected by
the virus or that containment and prevention would have been easier, what is
quite evident is that the overall economic impact would have been less and recovery
would have been faster in such a fortune situation.













1 Comments
Interesting
ReplyDeletePlease share views in the comments.